Quickstart
Overview
By the end of this guide, you will be able to run Pysa to find bugs on most Python web servers, and view those bugs on Static Analysis Post Processor (SAPP).
This guide was tested on Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS, macOS 10.15.7, and Ubuntu 20.04 LTS on WSL1
If you run into any issues along the way, please refer to the common issues section to help you debug
Install dependencies
- Ubuntu
- macOS
Pysa runs on Pyre, so we require the same dependencies as Pyre. You will need Python 3.9 or later, and setuptools and wheel Python packages.
$ python3 -m pip install --upgrade setuptools
$ pip3 install wheel
Since the Python version included in Ubuntu 18.04.5 is Python 3.6.9, we will need to update Python to a newer version.
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt install python3.9 python3.9-venv python3.9-dev python3-pip -y
Next we need to install setuptools and wheel python packages:
$ python3.9 -m pip install --upgrade setuptools
$ pip3 install wheel
Initial configuration
- Set up the virtual environment:
$ python3 -m venv ~/.venvs/pysa
$ source ~/.venvs/pysa/bin/activate
- Install Pyre and SAPP in the virtual environment:
(pysa) $ pip install pyre-check fb-sapp
- Initialize Pysa and SAPP
You can quickly setup a suitable environment to run Pysa and SAPP with the following command:
(pysa) $ pyre init-pysa
This command setups sets up your repo to run Pysa and provides some optional tweaks to your repo to improve Pysa's results.
Run Pysa
Now that Pysa is set up to run on your project, you won't need to repeat any of the earlier steps to run Pysa on subsequent runs. You can run Pysa with pyre analyze.
(pysa) $ pyre analyze --no-verify --save-results-to ./pysa-runs
This command will run Pysa and store the results of the Pysa run into a pysa-runs folder in your project directory. The output of Pysa runs will be used later by SAPP to help you filter and refine the results Pysa provides you.
Run SAPP
After you have the results from your Pysa run stored in pysa-runs, we will ingest those runs into SAPP for analysis with the following command:
(pysa) $ sapp analyze ./pysa-runs/taint-output.json
We imported some filters into SAPP earlier and now that SAPP has processed your latest Pysa run, you can run the following command to spawn the server for the SAPP Web UI at http://localhost:5000:
(pysa) $ sapp server
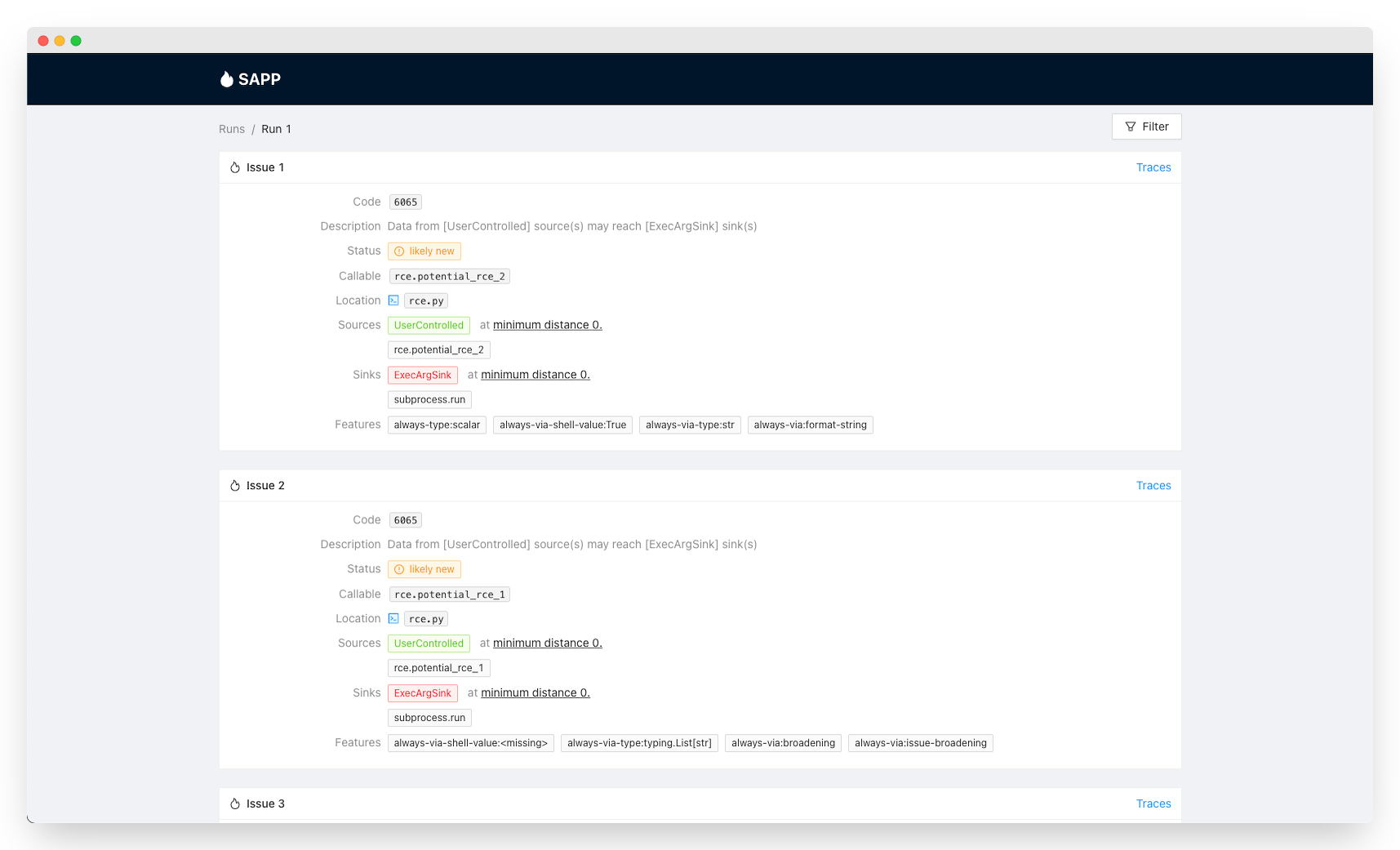
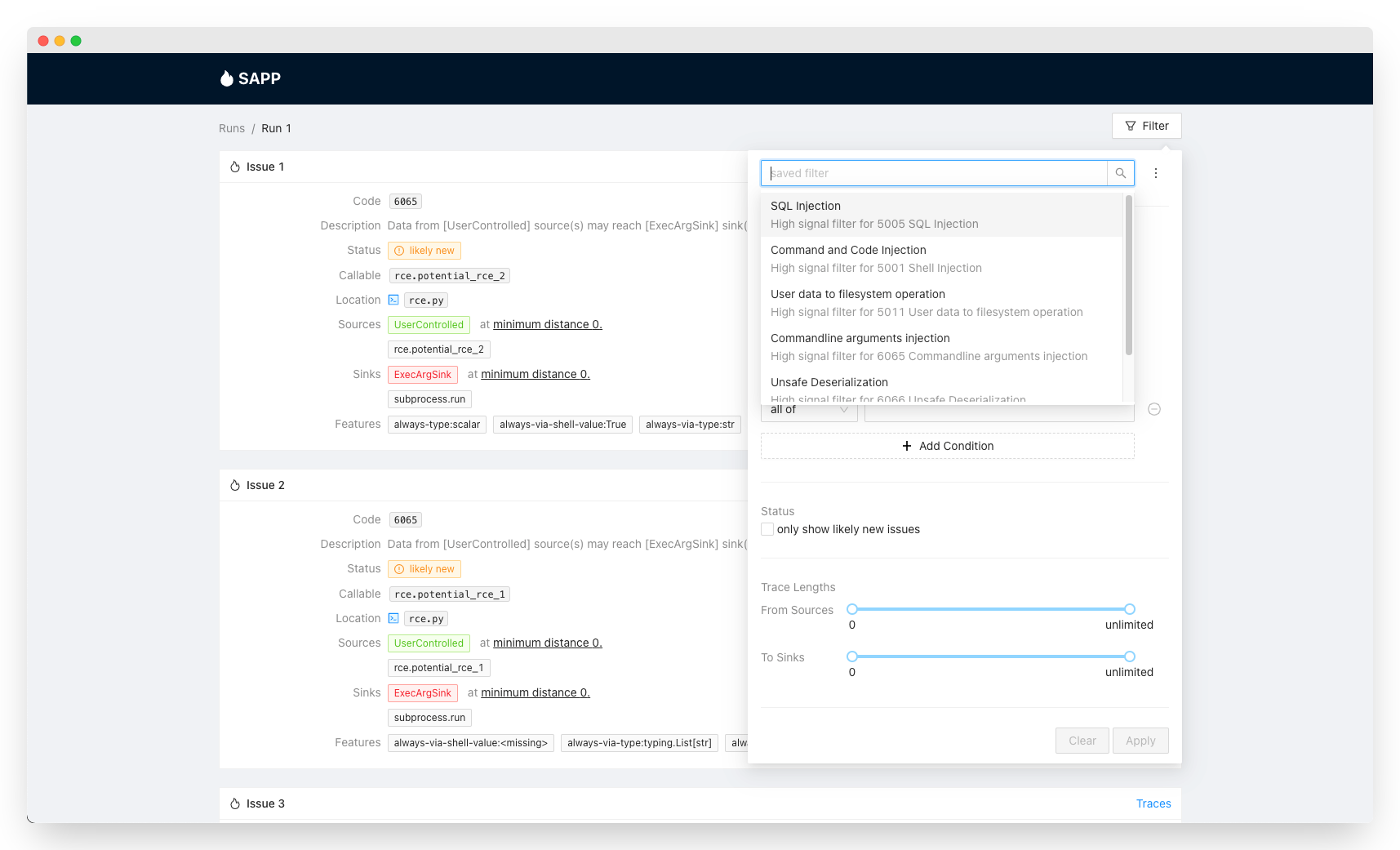
Through SAPP's Web UI, you can view and filter the issues Pysa found by clicking on the "Filter" button. A list of filters should appear under "Saved Filters" for you to choose from. Note that unfiltered Pysa issues can be noisy by default, so it is usually preferable to browse issues via these saved filters.
Going beyond the basics
We've provided you with some filters in SAPP to help you find a small subset of the bugs Pysa is able to catch. If you want to use Pysa to its full potential and find more bugs than the ones in your current Pysa run, you can learn how to write your own filters and tailor Pysa for your codebase below:
- Introduction to Pysa
- DEF CON 28 Pysa Tutorial
- Pysa Debugging False Positives and Negatives
- SAPP Documentation
Common Issues
Problem: Installing my project dependencies while in my virtual environment gives me errors, because some of my project dependencies are not compatible with Python 3+.
Solution: Fortunately, you can still run Pysa and SAPP on your project, so feel free to continue with the Quickstart instructions. However, Pysa may miss some taint flows.
Problem: pip install fb-sapp or pip install pyre-check results in ERROR: Could not install packages due to an OSError: [Error 13] Permission denied
Solution: Likely you are not installing fb-sapp or pyre-check in the virtual environment we created earlier. Try running source ~/.venvs/pysa/bin/activate before running pip install.
$ source ~/.venvs/pysa/bin/activate
(pysa) $ pip install pyre-check
Problem: pip install fb-sapp or pip install pyre-check fails, because it has multiple compilation errors like
fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory
#include <Python.h>
^~~~~~~~~~
compilation terminated.
error: command 'x86_64-linux-gnu-gcc' failed with exit status
Solution: You are missing setuptools python package or python3.9-dev
$ sudo apt install python3.9-dev -y
$ source ~/.venvs/pysa/bin/activate
$ (pysa) python3 -m pip install --upgrade setuptools
Problem: Attempting to create a virtual environment with python3 -m venv ~/.venvs/pysa results in The virtual environment was not created successfully because ensurepip is not available.
Solution: You are either missing python3.9-venv or python3.9-dev package. Make sure you delete the directory created by the failed virtual environment command earlier.
$ sudo apt install python3.9-venv python3.9-dev -y
$ rm -rf ~/.venvs/pysa
$ python3 -m venv ~/.venvs/pysa
Problem: Running pip install fb-sapp or pip install pyre-check fails to install, because of a series of error: invalid command 'bdist_wheel' errors
Solution: You are missing either wheel or setuptools package
$ (pysa) pip3 install wheel
$ (pysa) python3 -m pip install --upgrade setuptools
Problem: pyre init-pysa shows ƛ Source directory path/to/dir does not exist. Be sure the source path is relative to the import_root.
Solution: You will need to manually update source_directories in .pyre_configuration. Refer to Pyre Global configuration section to set up source_directories.
Problem: Running pyre analyze --no-verify command results in ƛ Error: Could not find a pyre client.
Solution: Some shells (e.g. zsh) require a restart to pick up updated PATH variables.
For example:
(pysa) $ pip install pyre-check
(pysa) $ cd demo-project
(pysa) $ pyre analyze --no-verify
ƛ Error: Could not find a pyre client.
(pysa) $ which pyre
/usr/local/bin/pyre
which pyre points to a path not within the virtual environment (e.g. /usr/local/bin)
(pysa) $ deactivate
(pysa) $ zsh
$ source ~/.venvs/pysa/bin/activate
(pysa) $ which pyre
/Users/unixname/.venvs/pysa/bin/
which pyre now points to a path in the virtual environment (e.g. ~/.venvs/pysa/bin/)
Ideally, if you have a local installation of Pyre, it would be best to remove the installation and only install Pyre in a virtual environment.
Problem: Running pyre analyze results in a bunch of errors and Pysa stops running
Solution: Run pyre analyze --no-verify to skip model validation.
Problem: Running pyre analyze --no-verify will freeze when parsing stubs and sources or processing functions, but the seconds runtime timer is still increasing
Solution: Unfortunately, it is likely the case that your machine doesn't have enough memory to run Pysa on projects with similar size to yours.
Problem: pyre analyze --no-verify exits with error ƛ Uncaught exception: (Invalid_argument "~/.venvs/pysa/lib/pyre_check/typeshed/stdlib/zlib.pyi is not a directory")
Solution: Delete your virtual environment and recreate your virtual environment by following the steps in the Initial configuration section
(pysa) $ deactivate
$ rm -rf ~/.venvs/pysa
Problem: I'm seeing a bunch of errors like ~/.venvs/pysa/lib/pyre_check/taint/filename.pysa: module.path.function_name is not part of the environment!
Solution:
If you don't use the module.path.function_name mentioned in your project, you can ignore them. Pysa ships with many taint models for code that isn't present in all projects. The errors you are seeing is Pysa informing you that Pysa hasn't found the source code for that particular function in your project or your venv.
If you do use the module.path.function_name mentioned in your project and the package wasn't installed with pip, you will need to add the package's path to search_path in your .pyre_configuration. Eventually, your .pyre_configuration should look something like this:
{
"source_directories": [
"."
],
"search_path": [
"path/to/external/library"
],
"taint_models_path": "~/.venvs/pysa/lib",
}
Problem: Running any sapp command results in SyntaxError: future feature annotations is not defined
Solution: SAPP requires Python 3.9. Ensure you are running a Python version later than Python 3.9
$ python3 --version
Problem: Running any sapp command results in a bunch of SAWarnings like
SAWarning: SAWarning: relationship 'Child.parent' will copy column parent.id to column child.parent_id, which conflicts with relationship(s): 'Parent.children' (copies parent.id to child.parent_id). If this is not the intention, consider if these relationships should be linked with back_populates, or if viewonly=True should be applied to one or more if they are read-only. For the less common case that foreign key constraints are partially overlapping, the orm.foreign() annotation can be used to isolate the columns that should be written towards. The 'overlaps' parameter may be used to remove this warning.
Solution: Please ignore the SAWarnings. They don't affect the functionality of SAPP and everything should be working as intended.
Problem: I can't connect to the Web UI and it displays an error related to SSL. The SAPP server log displays a bunch of 400 Bad Request error codes
Solution: Make sure you are visiting http://localhost:5000 and not https://localhost:5000
Problem: If your SAPP server shows 404 Not found and the webpage shows The requested URL was not found on the server. If you entered the URL manually please check your spelling and try again.
Solution: The SAPP Web UI will show this error when there are no issues imported during sapp analyze. Check if Pysa has found any issues with your project and if SAPP has imported any of those issues.
Checking if Pysa found any issues - you should expect the following command return at least one line:
(pysa) $ cat taint-output.json | grep "issue"
Checking which issues SAPP imported - you should expect the following lines to appear after running sapp analyze:
(pysa) $ sapp analyze
[INFO] Parsing analysis output...
[INFO] Generating issues and traces
[INFO] Run starting...
[INFO] Preparing bulk save.
[INFO] Dropped 0 unused TraceKind.precondition, 0 are missing
[INFO] Dropped 6 unused TraceKind.postcondition, 0 are missing
[INFO] Saving 10 issues, 21 trace frames, 0 trace annotations, 50 trace frame leaf assocs
...
[INFO] Run finished (0:00:00)
Problem: The issues on SAPP Web UI have boxes with No file found for filename.py, so I cannot see the source code related to the trace for my issues
Solution: Try passing the path to your project source code with --source-directory to sapp server
(pysa) $ sapp server --source-directory path/to/project_source_code
Problem: Pysa still doesn't work despite trying everything above
Solution: Ensure you are not running a nightly version of Pyre
(pysa) $ pip uninstall pyre-check-nightly
(pysa) $ pip install pyre-check
Some shells (e.g. zsh) will require extra steps:
(pysa) $ pip uninstall pyre-check-nightly
(pysa) $ deactivate
$ zsh
(pysa) $ source ~/.venvs/pysa/bin/activate
(pysa) $ pip install pyre-check
If you are still unable to get Pysa to run, please file an issue on pyre-check GitHub repo with some information about what OS you are running on, what error you are running into, and how to reproduce the error.